Generate color noise using Auto-Regressive (AR) model
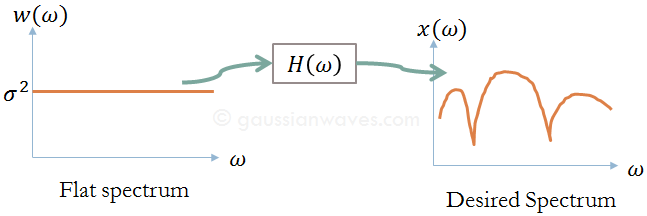
Key focus: Learn how to generate color noise using auto regressive (AR) model. Apply Yule Walker equations for generating power law noises: pink noise, Brownian noise. Auto-Regressive (AR) model An uncorrelated Gaussian random sequence \(x[n]\) can be transformed into a correlated Gaussian random sequence \(y[n]\) using an AR time-series model. If a time series random … Read more